What Happens if All the Chromosome Kinetochores Are Not Attached
While the attachment of DNA to microtubules is clearly a fundamental role of kinetochores we are only beginning to elucidate the specific. As previously mentioned the centromere is easily visualized as the most constricted region of a condensed mitotic chromosome.

Kinetochore Microtubule Capture And Chromosome Congression A Download Scientific Diagram
What happens if all the chromosome kinetochores are not attached to spindle fibers.

. The centrioles can be found at the opposite poles of the cell. Failure of kinetochores to bind to spindle microtubules or incorrect association such as when both sister kinetochores attach to microtubules from the same spindle pole results in mitotic delay or arrest. The cell is lengthened and elongated by spindle fibers that are not attached to chromatids.
A kinetochore is a protein structure that forms on a chromatid during cell division and allows it to attach to a spindle fiber on a chromosome. What happens if all the chromosome kinetochores are not attached to spindle fibers. Anaphase the separation of sister chromatids does not begin until all the chromosomes are properly attached to the spindle at the metaphase plate.
Although the molecular mechanisms that couple microtubule binding to. Some proteins for example mitotic arrest-deficient protein 2 MAD2 may monitor microtubule binding to. Although the word centromere is derived from the Greek words centro central and mere part centromeres are not always found in the center of chromosomes.
For this reason most of the times the second kinetochore becomes attached to the microtubules emanating. The daughter chromosomes travel to the poles at opposing ends of the cell through the spindle machinery. During anaphase the paired chromosomes sister chromatids split and begin to move to opposing ends of the cell poles.
It is thought that unattached or improperly attached kinetochores generate a signal to prevent premature progression to anaphase even if most of the kinetochores have been attached and most of the. As chromosomes have two kinetochores associated back-to-back one on each sister chromatid when one of them becomes attached to the microtubules generated by one of the cellular poles the kinetochore on the sister chromatid becomes exposed to the opposed pole. Kinetochores form attachments to microtubule ends no easy feat since microtubules are constantly growing and shrinking they sense tension to ensure that sister chromatids are connected to microtubules from opposite poles and they signal the cell to stop.
Kinetochores are important elements of a mitotic checkpoint. The kinetochore a protein complex on the chromosome is key to regulating chromosome segregation. Growth factor is a protein released by certain cells that stimulates other cells to.
Upon attachment kinetochores move chromosomes on the spindle generating tension. Only when the kinetochores are all properly attached to the spindle does the appropriate regulatory protein complex become active. If all the chromosome kinetochores are not attached to spindle fibers the sister chromatids remain together delaying anaphase.
When this occurs which checkpoint is not passed. Depletion of SAC proteins from kinetochores attached to spindle microtubules is likely to be a mechanistically relevant step in SAC extinction because constitutive targeting of Mad1 to the kinetochore is sufficient to sustain Mad2-dependent SAC signaling after chromosome bi-orientation 57. When this occurs the M phase checkpoint is not passed.
Spindle fibers growing outward can be seen and these have attached to all chromosome kinetochores at the. In the absence of proper chromosome attachment and spindle tension checkpoint mechanisms prevent progression through mitosis. Click to see full answer.
When this occurs the M-phase checkpoint is not passed. This condition keeps the cell from passing the M checkpoint.

Chromosome Segregation Correcting Improperly Attached Chromosomes Current Biology
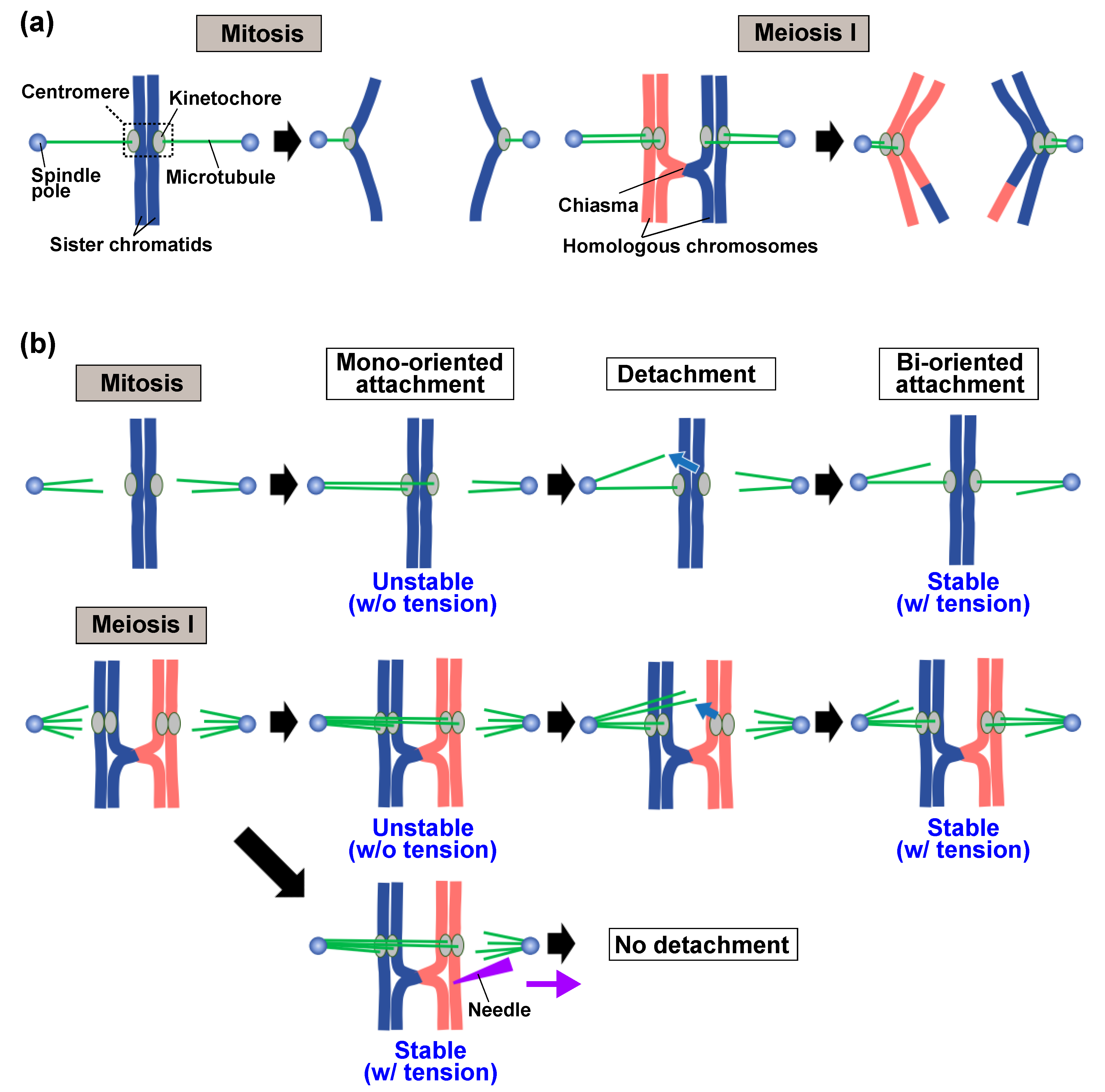
Ijms Free Full Text Shake It Off The Elimination Of Erroneous Kinetochore Microtubule Attachments And Chromosome Oscillation Html

Reduced Stability Of Kinetochore Microtubule Attachment In Anaphase In Download Scientific Diagram

C5 Gcse Biology Mitosis Meiosis Teaching Biology Biology Notes School Notes

The Kinetochore In M Phase A Mitotic Chromosome Segregation And A Download Scientific Diagram

Regulation Of Chromosome Segregation In Eukaryotes During Download Scientific Diagram

Regulation Of A Dynamic Interaction Between Two Microtubule Binding Proteins Eb1 And Tip150 By The Mitotic P300 Cbp Associated Factor Pcaf Orchestrates Kinetochore Microtubule Plasticity And Chromosome Stability During Mitosis Journal Of

Chromosome Segregation During Mitosis And Meiosis A Pathways To Download Scientific Diagram
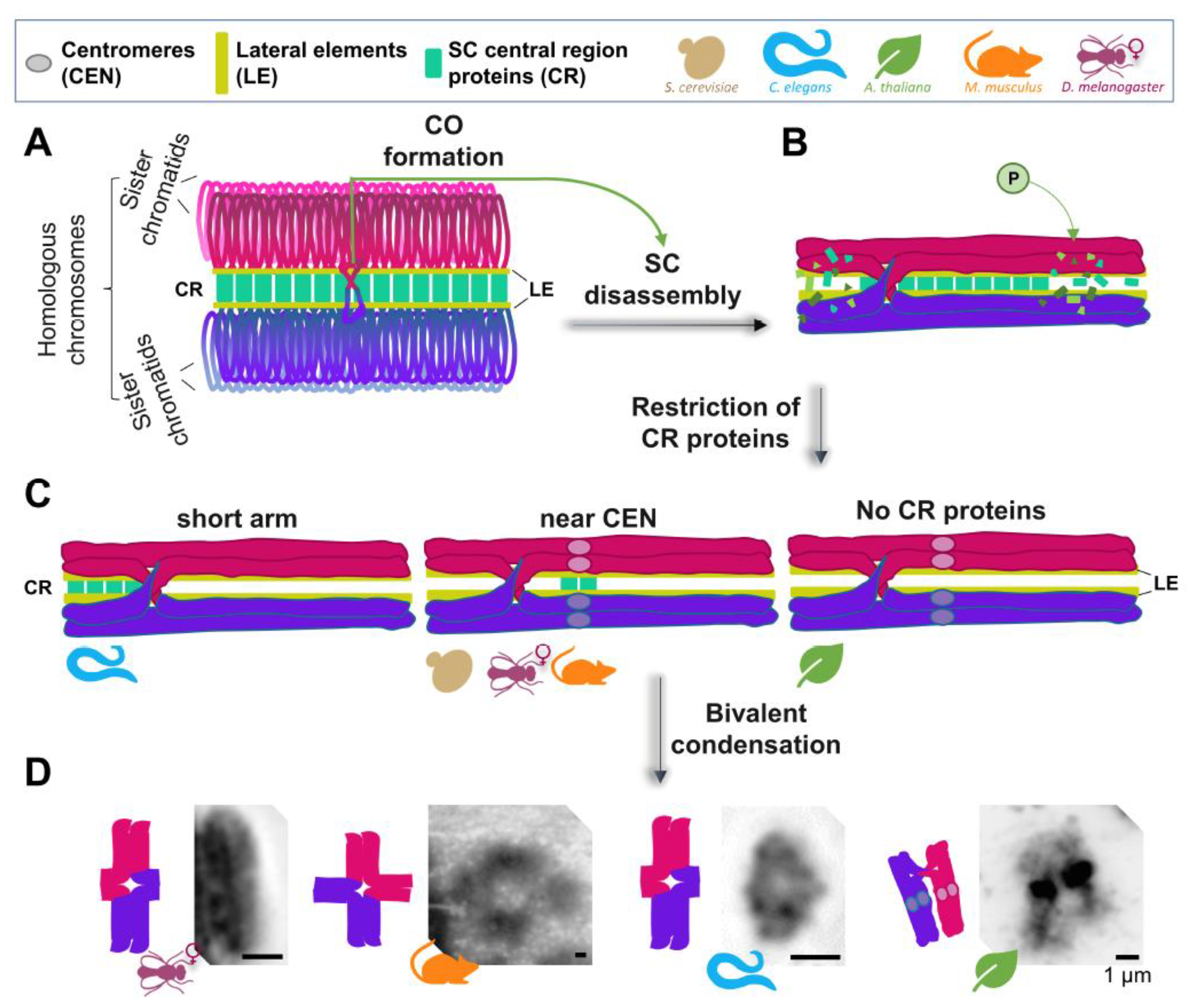
Genes Free Full Text Loss Gain And Retention Mechanisms Driving Late Prophase I Chromosome Remodeling For Accurate Meiotic Chromosome Segregation Html

Mechanisms And Effects Of Chromosome Segregation Errors In Mitosis A Download Scientific Diagram

The Kinetochore In M Phase A Mitotic Chromosome Segregation And A Download Scientific Diagram

Perpetually Uncongressed Chromosomes Are Not Syntelically Attached A Download Scientific Diagram

Chromosome Movement Dynein Out At The Kinetochore Current Biology

A Condensed View Of The Chromosome Passenger Complex Trends In Cell Biology

Lytic Vs Lysogenic Cycle Genome Chromosome Genetics
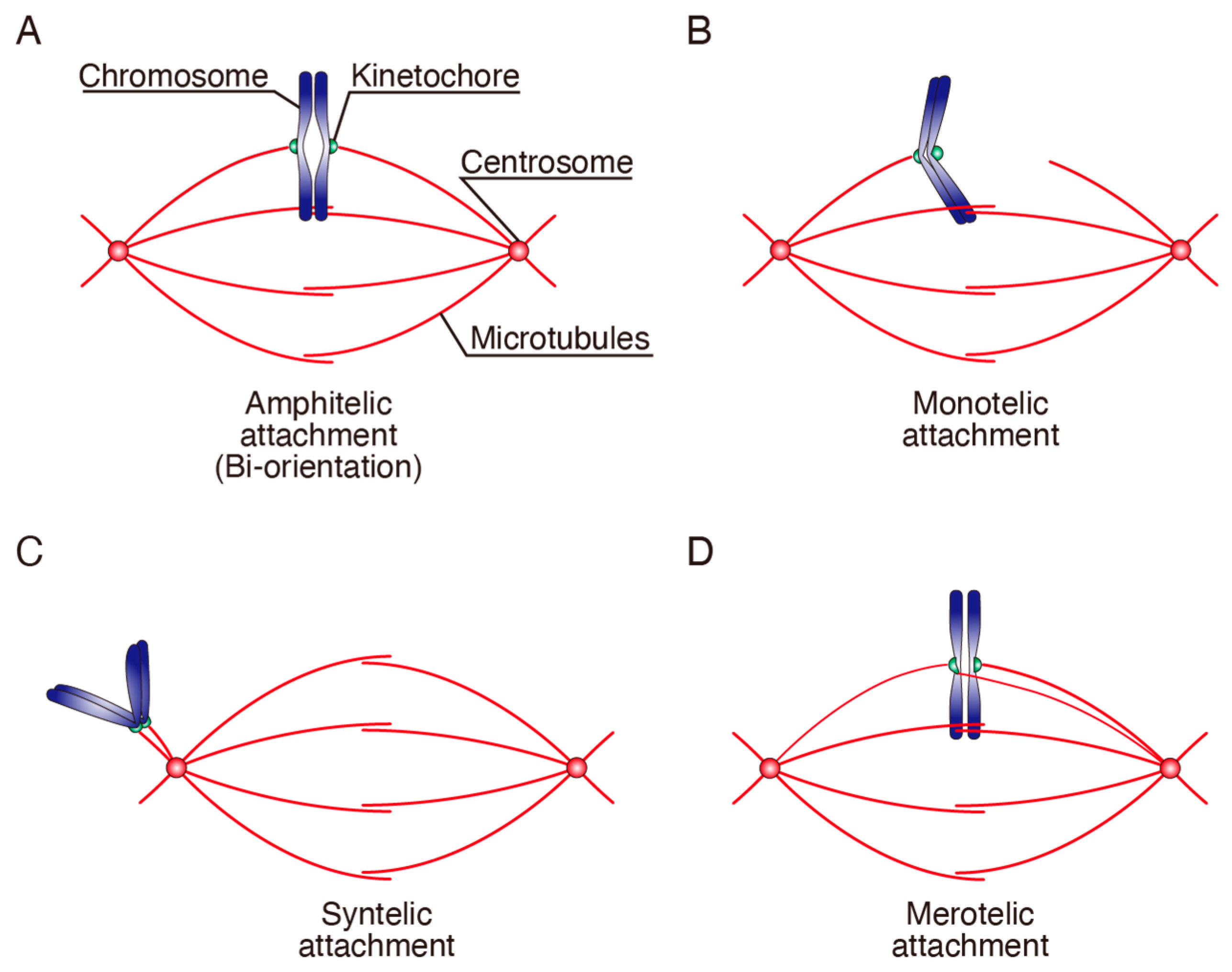
Cancers Free Full Text Attenuated Chromosome Oscillation As A Cause Of Chromosomal Instability In Cancer Cells Html
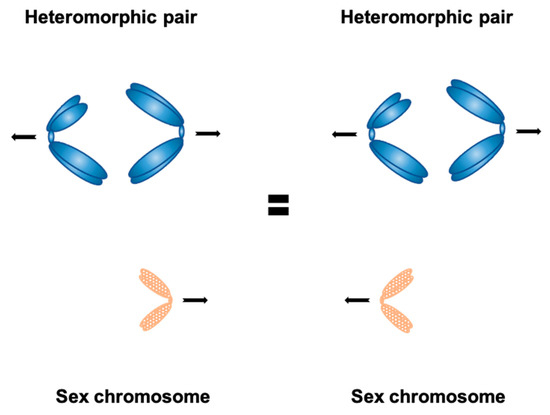
Genes Free Full Text Flavors Of Non Random Meiotic Segregation Of Autosomes And Sex Chromosomes Html

Kinetochore Stretching Mediated Rapid Silencing Of The Spindle Assembly Checkpoint Required For Failsafe Chromosome Segregation Sciencedirect

Budding Yeast Mps1 In The Control Of Chromosome Biorientation In Wild Download Scientific Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment